A Guide to Building Earthquake-Resistant Structures
Earthquakes are natural disasters that can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure. Building earthquake-resistant structures is crucial to mitigate the impact of seismic events and protect lives and property.
Understanding Earthquakes
Earthquakes occur due to the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, usually caused by the movement of tectonic plates. The seismic waves generated by earthquakes can exert tremendous force on buildings, leading to structural failure and collapse.
Principles of Earthquake-Resistant Design
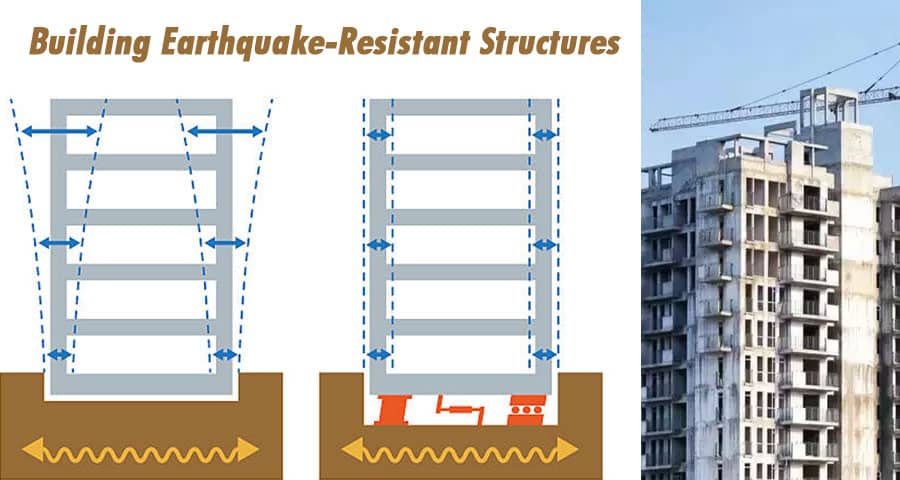
Designing earthquake-resistant structures involves implementing various principles to withstand the dynamic forces generated by earthquakes. Base isolation, damping systems, and flexible structural designs are key strategies used to enhance seismic performance.
Materials for Earthquake Resistance
Selecting appropriate construction materials is essential for ensuring the earthquake resistance of buildings. Materials such as reinforced concrete, steel, and masonry offer strength and flexibility to withstand seismic forces.
Design Considerations
Effective earthquake-resistant design considers factors such as foundation design, structural systems, and the symmetry and regularity of building configurations. These considerations help distribute seismic loads evenly and prevent concentrated stress points.
Construction Techniques
Construction techniques play a crucial role in building earthquake-resistant structures. Methods like reinforced concrete frames, shear walls, and cross-bracing provide structural stability and resilience against seismic forces.
Building Codes and Regulations
Adherence to building codes and regulations is paramount in ensuring the seismic safety of structures. International standards and local regulations dictate minimum requirements for seismic design and construction practices.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Thorough testing and quality assurance procedures are essential to verify the seismic performance of buildings. Simulation tests and field testing help assess structural integrity and identify potential weaknesses.
Maintenance and Retrofitting
Regular maintenance and retrofitting of existing structures are necessary to enhance their earthquake resistance. Inspections and structural upgrades can improve the seismic performance of buildings and prolong their lifespan.
Case Studies
Examining successful examples of earthquake-resistant structures provides valuable insights into effective design and construction practices. Case studies highlight innovative solutions and best practices in seismic resilience.
Cost Considerations
While building earthquake-resistant structures may incur higher initial costs, the long-term benefits outweigh the investment. The economic impact of earthquake damage far exceeds the expenses associated with seismic design and construction.
Community Preparedness
Community preparedness plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of earthquakes. Public awareness campaigns, emergency response planning, and infrastructure resilience initiatives help communities become more resilient to seismic events.
Challenges and Future Trends
Addressing challenges such as rapid urbanization and advancing technology is essential for improving earthquake resilience. Innovations in construction materials and techniques offer promising opportunities for enhancing seismic performance in the future.
Conclusion
Building earthquake-resistant structures is essential for safeguarding lives and property against the devastating effects of seismic events. By incorporating sound design principles, construction techniques, and community preparedness measures, we can create safer and more resilient built environments.
FAQs
What makes a building earthquake-resistant?
Earthquake-resistant buildings are designed and constructed using materials and techniques that can withstand seismic forces without significant damage.
Are all earthquake-resistant structures expensive to build?
While some earthquake-resistant structures may require higher initial investments, the long-term benefits in terms of safety and reduced damage outweigh the costs.
How do earthquakes affect different types of buildings?
Earthquakes can affect buildings differently depending on factors such as their design, construction materials, and proximity to the epicenter. Structures with flexible designs and robust construction tend to fare better during seismic events.
Can old buildings be made earthquake-resistant?
Yes, old buildings can be retrofitted to improve their earthquake resistance. Retrofitting involves strengthening existing structures to meet modern seismic safety standards.
What role do building codes play in earthquake resilience?
Building codes establish minimum requirements for seismic design and construction, ensuring that structures are built to withstand anticipated seismic forces and minimize the risk of collapse during earthquakes.
